Introduction to Kubernetes.
Kubernetes (k8s) is an open-source container orchestration engine developed by Google. Kubernetes managing containerized application workloads and service, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. Kubernetes configuration (manifest) file can be written in YAML and JSON formats.
What is Container Orchestration?
Container Orchestration is all about managing the life
cycles of containers, especially in large, dynamic environments.
Why we used Container Orchestration.
Container Orchestration can be used to perform lot of tasks,
some of them includes:
1. Provisioning and deployment of containers.
2. AutoScaling :- Scaling up or removing containers to spread application load evenly. (vertical and Horizontal)
3. Platform Independent :- Movement of containers from one host to another if there is a shortage of resources.
4. Load Balancing of service discovery between
containers.
5. Health monitoring of containers and hosts.
Rollback :- Can go back to previous version.
Batch execution :- one time, sequential, Parallels.
Fault Tolerance :- node and pods failure.
Container Orchestration Solutions which are available,
some of the popular ones include:
1.
Docker Swarm.
2.
Kubernetes.
3.
Apache Mesos.
4.
Elastic Container service (AWS ECS).
5. Elastic Kubernetes service (AWS EKS).
Few of the methods of install kubernetes.
Kubeadm -Multi-Node Cluster in our own premises.
Kubernetes Master Node
Kubernetes Master is a main node responsible for managing the entire kubernetes clusters. It handles the orchestration of the worker nodes.
1. Web UI (Dashboard)
Dashboard is a web-based Kubernetes user interface. You can use Dashboard to deploy containerized applications to a Kubernetes cluster, troubleshoot your containerized application, and manage the cluster itself along with its attendant resources.
2. Kubectl.
Kubectl is a command line configuration tool (CLI) for Kubernetes used to interact with master node of kubernetes. Kubectl has a config file called kubeconfig, this file has the information about server and authentication information to access the API Server.
3.API Server.
Kube API Server interacts with API, Its a frontend of the kubernetes control plane. API for almost every operation User interact with these API using a tool call Kubectl or UI through a dashboard.
The Kubernetes API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of HTTP endpoints that allow you to interact with a Kubernetes cluster.
The API serves as the communication interface between different components of Kubernetes and enables users to control and manage various aspects of the cluster.
4.Scheduler.
Scheduler watches the pods and assigns the pods to run on specific hosts.
5. cloud-controller-manager.
Same as kube-controller manager but for cloud service.
i) Node Controller :-
ii) Route Controller :-
iii) Service Controller :-
iv) Volume Controller :-
6.Kube-Controller-Manager.
Controller manager runs the controllers in background which runs different tasks in Kubernetes cluster.
i). Node controller - Its responsible for noticing and responding when nodes go down.
ii). Replication controllers - It maintains the number of pods. It controls how many identical copies of a pod should be running somewhere on the cluster.
iii). Endpoint controllers joins services and pods together.
iv). Token controllers - Services account and Token controllers handles access managements.
v). ReplicaSet controllers ensure number of replication of pods running at all time.
vi). Deployment controller provides declarative updates for pods and replicasets.
vii). Daemonsets controller ensure all nodes run a copy of specific pods.
viii). Jobs controller is the supervisor process for pods carrying out batch jobs Services allow the communication.
Namespace
CronJob
StatefulSet
etcd is a simple distribute key value store. Kubernetes uses etcd as its database to store all cluster data's. Some of the data stored in etcd is job scheduling information, pods, state information and etc.
etcd is consistent and high-available store.
Fully replicated :- The entire state is available on every node in the cluster.
Secure :- Implements automatic TLS with optional client certificate authentication.
Fast :- Benchmarked at 10,000 writes per sec.
Worker Nodes
Worker nodes are the nodes where the application actually
running in Kubernetes cluster, it is also know as minion. These each worker
nodes are controlled by the master node using kubelet process.
Container Platform must be running on each worker nodes
and it works together with kubelet to
run the containers, This is why we use Docker engine and takes care of managing
images and containers. We can also use other container platforms like CoreOS,
Rocket.
Requirements of Worker Nodes:
1.
kubelet.
2.
Docker container.
3.
kube-proxy.
4. supervisord
1.
Kubelet
Kubelet is the primary node agent runs on each nodes and reads the container manifests which ensures that containers are running and healthy.
2.
Kube-proxy
Kube-proxy is a process helps us to have
network proxy and loadbalancer for the services in a single worker node. It
performs network routing for tcp and udp packets, and performs connection
folding. Worker nodes can be exposed to internet via kubeproxy.
Minion
These are the slave nodes which serve/run app as requested/deployed by the user and Kubernetes master.
Label
an arbitrary key/value pair that the Replication Controller uses for service discovery.
Service
an endpoint that provides load balancing across a replicated group of pods
Installing Kubernetes on ubuntu 18.04
1. Minimum requirement for Kubernetes testing.Master Node :-
CPU - 2 Core, Memory -2 GB, HardDisk - 10 GB
Worker Node :-
CPU - 1 Core, Memory -1 GB, HardDisk - 10 GB
2. Swap memory disable all nodes.
# swapoff -a
3. /etc/hosts update file for all nodes.
172.31.4.18 worker1.example.com
172.31.14.200 worker2.example.com
# sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg-agent software-properties-common
# curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg |
sudo apt-key add -
# sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
# sudo apt-get update
# sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
# docker version
# sudo cat /sys/class/dmi/id/product_uuid
# sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y
apt-transport-https curl
# curl -s
https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
# cat <<EOF | sudo tee
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOF
# sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y
kubelet kubeadm kubectl
# kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
# mkdir -p
$HOME/.kube
# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
# kubectl get nodes
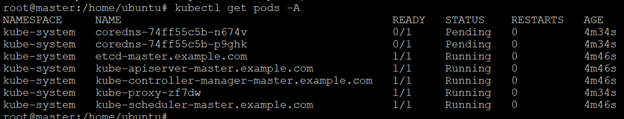
7. coredns pod status showing pending.
# kubectl get pods -A
8. Install Network Plugin.
NOTE :- https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/networking/#how-to-implement-the-kubernetes-networking-model
# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
# kubectl get pods -A
9. Now, add worker node in master node and command run only workers node.
# systemctl status kubelet
# kubeadm join 172.31.46.226:6443 --token
nohys3.drv6i33xzjlpr0o2 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash
sha256:1438d0cf353e5378b62aebb629d5a4f78d1c17aa8d95c6d58ccddbaf3adfe579
10. Will be check master node.
# kubectl get nodes
# kubectl get nodes -o wide
############### Kubernetes installation competed. ####################
Bash completion :-
# apt-get install bash-completion
# kubectl completion bash
# cd ~/.kube
# kubectl completion bash > kubecom.sh
# chmod +x kubecom.sh
# source $HOME/.kube/kubecom.sh
# vim ~/.profile
source $HOME/.kube/kubecom.sh
logout and login root user.
# kubectl get pods






No comments:
Post a Comment