Auto Scaling in Kubernetes (K8s).
Auto scaling in Kubernetes ensures that applications can
handle changing workloads by dynamically adjusting the number of pods or nodes.
There are three main types of auto scaling in
Kubernetes:
1️.Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
(HPA) – Scales pods based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics.
2️.Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) – Adjusts pod
resource requests & limits.
3️.Cluster Autoscaler (CA) – Adds or removes
worker nodes based on demand.
1️.Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) –
1.Enable Metrics Server:
Check if the Metrics Server is running:
# kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/download/v0.3.6/components.yaml
# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
# kubectl get deployment -n kube-system
# kubectl -n kube-system edit deployments.apps
metrics-server
command:
-
/metrics-server
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
-
--kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP
# kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l
k8s-app=metrics-server
# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
# kubectl logs -n kube-system -l k8s-app=metrics-server
# kubectl top nodes
# kubectl top pods -A
Or
# wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
# vim components.yaml
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP
# kubectl apply -f components.yaml
# kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep metrics-server
# kubectl logs -n kube-system -l k8s-app=metrics-server
# kubectl top nodes
# kubectl top pods -n <namespace>
2. Autoscale CPU-based HPA a Deployment.
# vim nginx-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name:
nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
cpu:
"100m"
limits:
cpu:
"200m"
ports:
-
containerPort: 80
requests: The guaranteed amount of CPU/Memory for
each pod.
limits: The maximum resources a pod can use before
being throttled.
100m (millicores) = 0.1 CPU core
200m (millicores) = 0.2 CPU core
1000m = 1 full CPU core
3.Create the Service (nginx-service.yaml)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
# kubectl apply -f nginx-deploy.yaml
# kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yaml
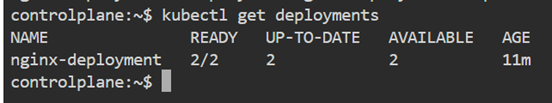
# kubectl get deployments
# kubectl get pods
# kubectl get svc
scaling between 2 and 5 pods when CPU utilization
exceeds 10% of the requested CPU.
# kubectl autoscale deployment <deloyment_name> --cpu-percent=10 --min=2 --max=5
# kubectl autoscale deployment nginx-deployment
--cpu-percent=10 --min=2 --max=5
#kubectl get hpa
4.Generate Load on Nginx.
kubectl run -it --rm load-generator --image=busybox --
/bin/sh -c "while true; do wget -q -O- http://nginx-service; done"
# kubectl describe hpa nginx-deployment
# kubectl delete vpa nginx-deployment
# kubectl delete -f components.yaml
Or
# kubectl delete -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/download/v0.3.6/components.yaml
# kubectl delete -f
nginx-deploy.yaml
# kubectl delete -f
nginx-service.yaml
HPA for
Memory Autoscaling.
Scale nginx-deployment between 2 and 5 pods.
Trigger scaling if average memory utilization exceeds 30%.
1.Create
an HPA for Memory Autoscaling.
# vim nginx-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name:
nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
cpu:
"100m"
memory: "20Mi" # Set memory request
limits:
cpu:
"200m"
memory: "30Mi" # Set memory limit
ports:
-
containerPort: 80
- requests:
The guaranteed amount of CPU/Memory for each pod.
- limits:
The maximum resources a pod can use before being throttled.
2.Create
an HPA YAML file.
i)Scale nginx-deployment between 2 and 5 pods.
ii)Trigger scaling if average memory utilization exceeds 25%.
# vim nginx-hpa.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: nginx-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion:
apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name:
nginx-deployment
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 5
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type:
Utilization
averageUtilization: 25 # Adjust this threshold as needed
# kubectl apply -f nginx-deploy.yaml
# kubectl top pods
# kubectl get hpa
4. Generate Memory Load to Trigger Scaling
Run a memory-intensive process in the Nginx pods:
# kubectl run -it --rm load-generator --image=busybox --
/bin/sh
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/null &
This will increase memory usage and trigger autoscaling.
# kubectl exec -it nginx-deployment-5d58ccd545-q8tdd --
/bin/bash
# kubectl exec -it nginx-deployment-5d58ccd545-88fvs --
/bin/bash
# kubectl get hpa
# kubectl get pods
# kubectl describe hpa nginx-hpa
Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) –
Unlike Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), which scales
the number of pods, VPA automatically adjusts CPU and memory requests/limits
for your pods based on usage.
How VPA Works:
- VPA
Recommender:
- Analyzes
historical resource usage and provides recommendations for CPU and memory
requests.
- VPA
Updater:
- Automatically
applies the recommended resource requests by evicting and restarting
pods.
- VPA
Admission Controller:
- Modifies
pod resource requests during pod creation to ensure they align with VPA
recommendations.
Modes of VPA:
- Auto:
- VPA
automatically applies resource recommendations and restarts pods as
needed.
- Initial:
- VPA
only applies recommendations when the pod is first created.
- Off:
- VPA
provides recommendations but does not apply them.
VPA for
Autoscaling.
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler.git
cd autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler
./hack/vpa-up.sh
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep vpa
for delete
./hack/vpa-down.sh
# kubectl delete -f vertical-pod-autoscaler/deploy/
# kubectl create namespace vpa-demo
Deploy an Application (Nginx).
# vim nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name:
nginx-deployment
namespace: vpa-demo
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
cpu:
"100m"
memory:
"128Mi"
limits:
cpu:
"200m"
memory:
"256Mi"
# kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
# kubectl get pods -n vpa-demo
Deploy VPA for Nginx
# vim nginx-vpa.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling.k8s.io/v1
kind: VerticalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: nginx-vpa
namespace: vpa-demo
spec:
targetRef:
apiVersion:
apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name:
nginx-deployment
updatePolicy:
updateMode:
"Auto" # VPA automatically
applies changes
resourcePolicy:
containerPolicies:
- containerName:
nginx
minAllowed:
cpu:
"50m"
memory:
"64Mi"
maxAllowed:
cpu:
"500m"
memory:
"512Mi"
controlledResources: ["cpu", "memory"]
# kubectl apply -f nginx-vpa.yaml
# kubectl get vpa -n vpa-demo
# kubectl describe vpa nginx-vpa -n vpa-demo
Target → The
recommended CPU & memory for optimal performance.
Lower Bound / Upper Bound → The minimum and maximum safe values.
Simulate High CPU Load (Trigger VPA).
# kubectl exec -it -n
vpa-demo nginx-deployment-57c44dfdb7-7jmgl -- /bin/bash
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/null &
# kubectl exec -it -n vpa-demo
nginx-deployment-57c44dfdb7-mfdv7 --
/bin/bash
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/null
What is the Difference Between VPA and HPA?
|
Feature |
VPA (Vertical Scaling) |
HPA (Horizontal Scaling) |
|
Adjusts |
CPU & Memory Requests |
Number of Pods |
|
Method |
Restarts pod with new resources |
Adds/Removes pods dynamically |
|
Best for |
Apps with unpredictable CPU/memory needs |
Apps with fluctuating traffic |
|
Feature |
VPA (Vertical Pod Autoscaler) |
ResourceQuota |
|
Scope |
Per Pod/Container |
Per Namespace |
|
Purpose |
Adjusts
pod resource requests and limits dynamically |
Enforces fixed
limits on total namespace resources |
|
Scaling Type |
Vertical
Scaling (adjusts CPU/memory per pod) |
Quota
Management (restricts overall usage in a namespace) |
|
Pod Restart? |
Yes (Pods
restart with new requests/limits) |
No, only
applies to new resource allocations |
|
Use Case |
Optimize
resource allocation for running workloads |
Prevent
excessive resource usage across multiple pods |
What is Cluster Autoscaler (CA)?
The Cluster Autoscaler (CA) is a Kubernetes component that automatically
scales worker nodes in a cluster up or down based on workload demands. It
ensures efficient resource utilization while optimizing costs.
i)Scales Up: Adds new nodes when there aren’t enough resources for pending pods.
ii)Scales Down: Removes underutilized nodes to save costs.
iii)Works with Auto Scaling Groups (ASG): On cloud platforms (AWS, GCP,
Azure, OpenShift).
✅ Cluster Autoscaler automatically scales nodes
up/down
✅ Works with cloud providers & can be
integrated with bare metal provisioning
✅ Prevents pending pods & removes
underutilized nodes to optimize costs
✅ Works best with Auto Scaling Groups (AWS, GCP,
Azure) or Metal³ (Bare Metal).
|
|
|
















No comments:
Post a Comment