What is a Kubernetes Job?
A Kubernetes
Job is used to create one or more pods that perform a specific task and then
terminate. Jobs are ideal for tasks that need to be run to completion, such as database
migrations, batch processing, or any task that needs to be executed once.
Core
Concepts Of Kubernetes Jobs:
- Completion: To be considered the task
completed, Pods are required to for confirming the Specifies
the desired number of completed.
- Pod Templates: To create the Pods that
will perform the actual tasks, it is required to Tasks use a pod template.
- Parallelism: This handles the maximum
number of pods that can run to execute tasks.
- Restart Policy: This is very useful, for the behavior of Pods, when the task fails, it can restart the task.
Key
Parameters in a Job:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Example Value |
|
backoffLimit |
Number of retries before marking Job as failed |
3 (default) |
|
completions |
pods creating one by one.
One pod task completed after that second pod task running. |
5 |
|
parallelism |
2 task running with
parallelism. |
2 |
|
activeDeadlineSeconds |
job duration limit is 10s if
jobs taken time 11s then jobs will be stop. |
600 (10 mins) |
|
ttlSecondsAfterFinished |
Time before Job is automatically deleted |
60 (1 min) |
|
restartPolicy |
Defines how pods restart on failure |
Never or OnFailure |
|
completionMode |
Specifies
how the Job tracks completions. |
NonIndexed or Indexed |
|
suspend |
If true,
the Job is suspended and will not create Pods. |
true or
false |
1️.backoffLimit
(Job Failure Retries).
- Defines how many times
Kubernetes retries a failed pod before giving up.
- Default is 6, but you can
set it lower to avoid infinite retries.
backoffLimit: 3 # Retry job 3 times before marking it as
Failed
2️.completions
(Total Required Successful Runs).
- Defines how many times
the Job must complete successfully.
- Example: If set to 5, five different
pods must complete successfully.
completions: 5 # Run 5 separate successful pods
3️.parallelism
(Number of Simultaneous Pods).
- Controls how many pods can
run in parallel at the same time.
- If parallelism is less than completions,
new pods start after others complete.
completions: 5
parallelism: 2 # Run only 2 pods at a time, even if 5
completions are needed
4️.activeDeadlineSeconds
(Time Limit for Job).
- Sets the max time a Job can run before it is
forcibly stopped.
- Useful to prevent Jobs
running forever due to a bug.
activeDeadlineSeconds: 600 # Stop Job after 10 minutes
5️.ttlSecondsAfterFinished
(Auto Cleanup Job).
- Automatically deletes the Job
after the specified time once it completes.
- Helps clean up old jobs
automatically.
ttlSecondsAfterFinished: 60 # Delete Job 1 minute after completion
6️.restartPolicy
(Pod Restart Behavior).
- Controls how failed pods restart
within a Job.
- Allowed values:
- Never (default) – Pod is not
restarted if it fails.
- OnFailure – Pod restarts if
it fails.
restartPolicy:
Never # Ensures a new pod is created
instead of restarting
1.default simple jobs.
# vim simple-job.yaml
apiVersion:
batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: simple-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
command: ["echo",
"Hello, Kubernetes!"]
restartPolicy: Never
# kubectl
apply -f simple-job.yaml
# kubectl get pods
# kubectl get jobs
# kubectl logs simple-job-gnxjh
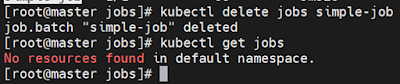
2.How to delete jobs.
# kubectl
delete jobs simple-job
3.pods creating one by one. One pod task completed after that
second pod task running.
completions: 2
# vim simple-job.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: simple-job
spec:
completions: 2
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
command:
["echo", "Hello, Kubernetes!"]
restartPolicy:
Never
# kubectl get jobs
# kubectl get pods
# kubectl logs simple-job-fdfwj
# kubectl logs simple-job-w7cm8
4.Parallel Jobs (Multiple Pods Running in
Parallel).
# cat
parallel-job.yaml
apiVersion:
batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: parallel-job
spec:
completions: 3 # Run 3
pods
parallelism: 3 # Run all
3 at the same time
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
image: busybox
command: ["sh",
"-c", "echo Processing; sleep 5"]
restartPolicy: Never
# kubectl
get jobs
# kubectl
get pods
5.test
directory is does not exist in busybox. If Jobs failed then pod creating again
and again.
backoffLimit: 2 # 2 time retry job if failed.
# vim simple-job.yaml
apiVersion:
batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: simple-job
spec:
backoffLimit: 2
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
command: ["ls", "/test"]
restartPolicy: Never
# kubectl
apply -f simple-job.yaml
# kubectl
get jobs.
# kubectl
get pods
# kubectl
describe jobs simple-job
6.job duration limit is 10s if jobs taken time 11s then jobs
will be stop.
activeDeadlineSeconds
# kubectl get jobs
# kubectl get pods
# kubectl describe jobs.batch time-limited-job
Cronjobs:
What is a Cronjob ?
CronJob is a higher-level controller that
allows you to schedule Jobs to run at specific times or
intervals, similar to how cron jobs work in Unix/Linux systems. CronJobs are
useful for automating repetitive tasks, such as backups, report generation, or
cleanup operations.
Default Save job history - 3
Default Save failed jobs history -1
Key Parameters in a CronJob:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Example Value |
|
schedule |
Defines when the CronJob runs (cron format) |
"*/5 * * * *" (Every 5
minutes) |
|
successfulJobsHistoryLimit |
Number of completed Jobs to keep |
3 (default: 3) |
|
failedJobsHistoryLimit |
Number of failed Jobs to keep |
1 (default: 1) |
|
concurrencyPolicy |
Controls overlapping Jobs |
"Allow" / "Forbid" / "Replace" |
|
startingDeadlineSeconds |
Time (in seconds) to allow Job to start late |
30 (30 seconds) |
|
suspend |
Temporarily stop Job execution |
true / false |
|
jobTemplate.spec.backoffLimit |
Number of retries before failing the Job |
3 |
|
jobTemplate.spec.activeDeadlineSeconds |
Maximum time before Job is stopped |
600 (10 mins) |
|
jobTemplate.spec.ttlSecondsAfterFinished |
Auto-delete Jobs after completion |
60 (1 min) |
|
|
|
|
1️.schedule (Defines When the Job Runs).
- Uses
cron syntax to set execution time.
- Example:
Run every 5 minutes.
spec:
schedule: "*/5
* * * *" # Every 5 minutes
2️.successfulJobsHistoryLimit & failedJobsHistoryLimit
(Job History Retention).
- Controls
how many completed or failed Jobs Kubernetes keeps.
- Helps
avoid excessive storage use.
spec:
successfulJobsHistoryLimit:
3 # Keep last 3 successful Jobs
failedJobsHistoryLimit:
1 # Keep only 1 failed Job
3️.concurrencyPolicy
(Handling Overlapping Jobs).
|
Value |
Behavior |
|
"Allow" |
Allows multiple Jobs to run at the same time (default). |
|
"Forbid" |
If the previous job run hasn't finished yet, the cron job
skips the new job run. If previous job
is completed then run other job. |
|
"Replace" |
If it is time for a new job run and the previous job run
hasn't finished yet, the cron job replaces the currently running job run with
a new job run. |
spec:
concurrencyPolicy: "Forbid" # Prevents overlapping Jobs
4️.startingDeadlineSeconds (Grace Period for Delayed
Execution).
- If
the Job is delayed, this sets the max time allowed before skipping
execution.
- Useful
when scheduling critical Jobs.
spec:
startingDeadlineSeconds:
30 # Job must start within 30 seconds or
be skipped=
5️.suspend
(Pausing Job Execution).
- If true,
suspends the CronJob without deleting it.
spec:
suspend: true # Stops the Job from running
6️.jobTemplate.spec.backoffLimit (Retries on Failure).
- How
many times Kubernetes retries a failed Job before marking it as
failed.
spec:
jobTemplate:
spec:
backoffLimit: 3 # Retry Job up to 3 times
7️.jobTemplate.spec.activeDeadlineSeconds (Max Job Execution
Time).
- Stops
the Job if it runs too long.
spec:
jobTemplate:
spec:
activeDeadlineSeconds:
600 # Stop Job if it runs longer than 10
minutes
8️.jobTemplate.spec.ttlSecondsAfterFinished (Auto-Cleanup).
- Automatically
deletes completed Jobs after a set time.
spec:
jobTemplate:
spec:
ttlSecondsAfterFinished:
60 # Delete Job 1 minute after
completion
1.default
cronjobs :- The cronjob is scheduled every minute.
The jobs is created and job will be create pod and
performing the task.
# cat jobs.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name:
example-cronjob
spec:
schedule: "*/1
* * * *" # Runs every minute
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name:
example-container
image:
busybox
command:
["echo", "Hello, Kubernetes!"]
restartPolicy: OnFailure
# kubectl get cronjobs
# kubectl get jobs
# kubectl describe
cronjob example-cronjob
2.successful
Jobs History Limit or failed Jobs history Limit.
successful Jobs History Limit :- completed jobs and
pods history deleting.
failed Jobs history Limit :- failed history jobs and
pods deleting.
# cat jobs.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name:
example-cronjob
spec:
schedule: "* *
* * *" # Runs every minute
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 1
failedJobsHistoryLimit: 1
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name:
example-container
image:
busybox
command:
["echo", "Hello, Kubernetes!"]
restartPolicy: Never
# kubectl apply -f jobs.yaml
# kubectl get cronjobs
# kubectl describe
cronjobs.batch example-cronjob
# kubectl get jobs.batch
3.How to
stop/suspending the cronjobs.
# kubectl edit cronjobs.batch example-cronjob
suspend:
true/false
OR
# kubectl patch cronjob example-cronjob -p
'{"spec":{"suspend":false}}'
3.TTL
controller :- TTL controller to clean up Jobs and Pods after they
completed job.
Jobs is completed then job will be deleted after 20sec.


















No comments:
Post a Comment